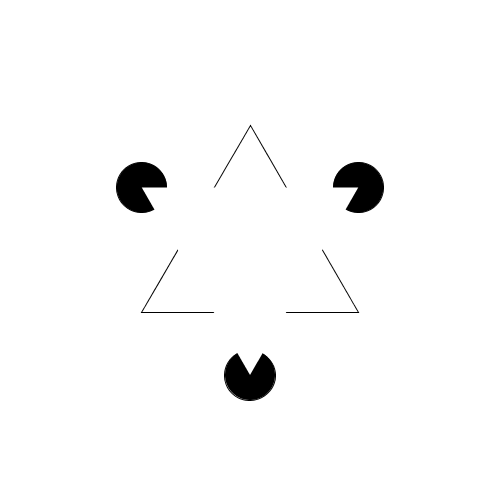
A classic example for the "Law of Closure".
int angle = 0;
PVector [] points = new PVector[3];
int counter = 0;
size(500,500);
translate(width/2,height/2);
while(counter < 3){
points[counter] = new PVector(cos(radians(angle + 30)) * width/4,sin(radians(angle+ 30))*width/4);
angle+=120;
counter++;
}
background(255);
//ellipse(0,0,width/2,height/2);
//ellipse(points[0].x,points[0].y,height/2,height/2);
//ellipse(points[1].x,points[1].y,height/2,height/2);
//ellipse(points[2].x,points[2].y,height/2,height/2);
triangle(points[0].x,points[0].y,points[1].x,points[1].y,points[2].x,points[2].y );
fill(0);
rotate(radians(180));
ellipse(points[0].x,points[0].y,width*0.1,width*0.1);
ellipse(points[1].x,points[1].y,width*0.1,width*0.1);
ellipse(points[2].x,points[2].y,width*0.1,width*0.1);
noFill();
//ellipse(points[0].x,points[0].y,height/2,height/2);
//ellipse(points[1].x,points[1].y,height/2,height/2);
//ellipse(points[2].x,points[2].y,height/2,height/2);
fill(255);
noStroke();
triangle(points[0].x,points[0].y,points[1].x,points[1].y,points[2].x,points[2].y );
saveFrame("out.png");